Today I found an online server in monitoring channel, alert saying Timtout connection to xxx.xxx.com which is one of our production entrance servers and then the story began …
1. Phenomenon and disk issue?
- It took me
over 4 secondsto SSH connect to this production server. For other production servers can be connected in less than 1 second. I also notice there are 50% packet loss to the target server. - Since this entrance server is very lack of disk, initially I was thinking it’s
disk issue, so I deleted some files and then restart the process.However, doesn't help. I started to think, it could be a network issue. - I noticed
kern.loghas error as next, and I steady confirmed it must be a network issue.nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packets.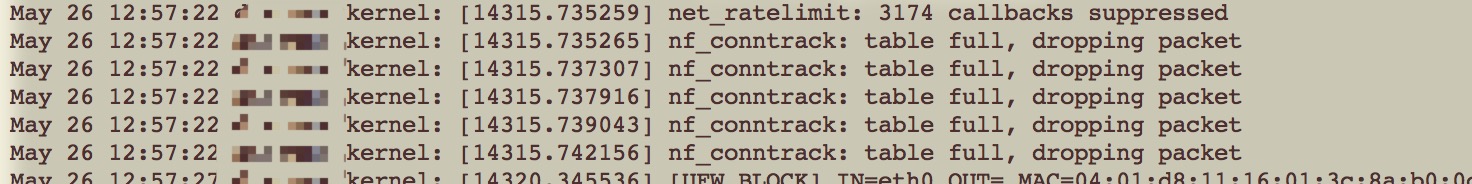
2. Solve the problem
After Googling it, I knew that conntrack is for stateful firewall.
Pls read Netfilter’s connection tracking system if you are interested. It also include the Netfilter framework basic.
So, in one word, conntrack is created to record connection state to inspect into traffic and avoid DDoS security issue.
2.1. Just tell me how to solve it
From the error above, we can know conntrack table is full. How to review the table size? By typing cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_count. We can get the size.1
2root@localhost:/# cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_count
76390
What’s the maximum size? You can get it by typing cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_max.
Let’s just increase it. Recommended size: CONNTRACK_MAX = RAMSIZE (in bytes) / 16384 / (ARCH / 32). Eg, I have 8GB RAM in x86_64 OS, so I made it as 8*1024^3/16384/2=262144, which is of course larger as the nf_conntrack_count.1
2sysctl -w net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=262144
echo "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=262144" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
Just after that, it works. Network latency becomes good now and no packet loss.
2.2. What if it really exceed this max limit?
- Option 1. We can remove the module of
state, but that will make iptables not providing with full compatible APIs. - Option 2. We can use
RAWiptable without usingCONNTRACKfeature.
RAW table is only applied toPREROUTINGandOUTPUTchain. Since it has the highest priority (raw-->mangle-->nat-->filter), so it can handle the connection before tracking mangement. Once after we handle the connection usingRAWtable, we will skipNAT tableandip_conntracthandler.
2.3. How to do without track state?
Review of IPtables,
iptableshas 4 tables and 5 chains as below graph:
- Tables: categorized by different operations to data packets.
raw: highest priority, only appied toPREROUTINGandOUTPUTchain. When we don’t need to do NAT, we can use RAW table to increase performance.mangle: modify certain data packetnat: NAT, port mapping, address mappingfilter: filter
- Chains: categorized by different hooks.
PREROUTING: packet before going to route tableINPUT: after packet passing route table, destination is current machineFORWARDING: after packet passing route table, destination is not current machineOUTPUT: packet comes from current machine and to outsidePOSTROUTIONG: packet before going to network interface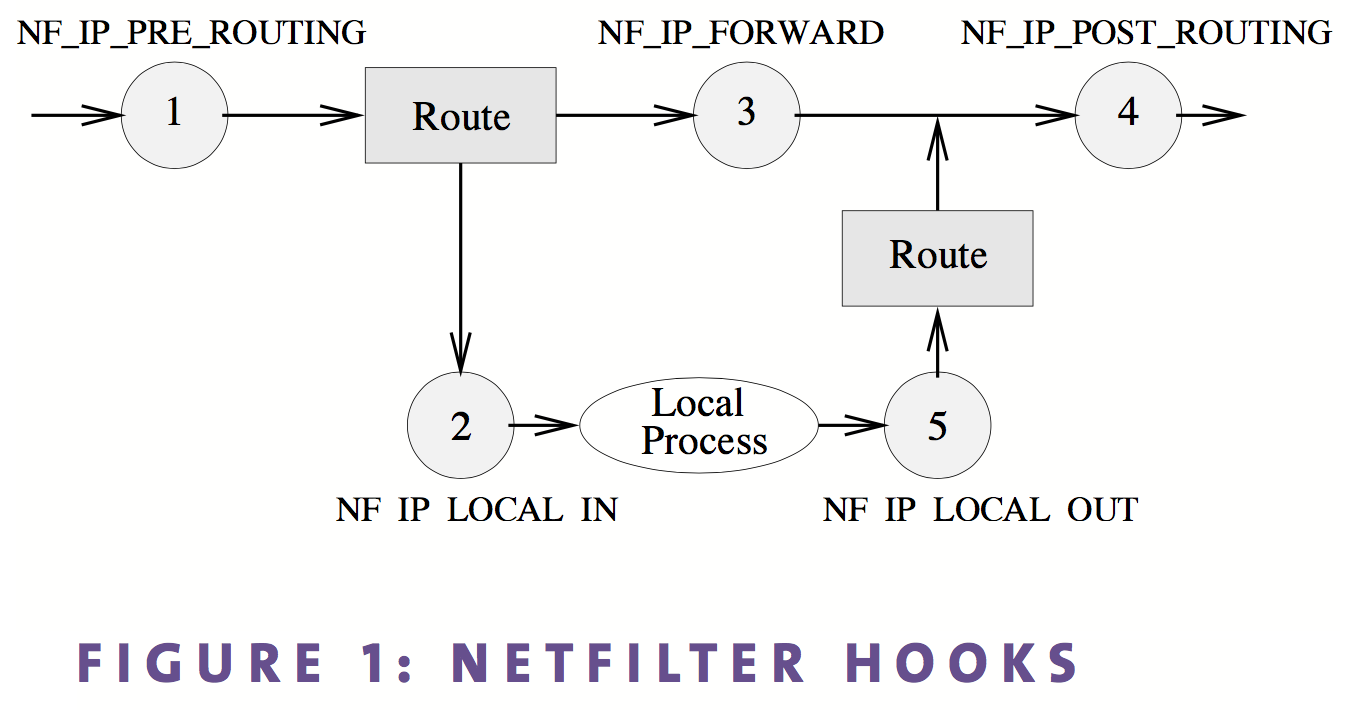
- Tables: categorized by different operations to data packets.
Mark
UNTRACKEDconnection will be accept:
CentOS: Change/etc/sysconfig/iptablesfile, and appendUNTRACKEDafter line ofRH-Firewall-1-INPUT.
To make it as-A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED,UNTRACKED -j ACCEPT
Other Linux :1
$ sudo iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state UNTRACKED -j ACCEPT
Use
rawtable rules on these ports.1
2
3
4
5# mark destination port and source port as NOTRACK
$ sudo iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p tcp -m multiport --dport 80,81,82 -j NOTRACK
$ sudo iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p tcp -m multiport --sport 80,81,82 -j NOTRACK
$ iptables -t raw -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,81,82 -j NOTRACK
$ iptables -t raw -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m multiport --sports 80,81,82 -j NOTRACKIf you have only one port, use
1
2
3
4$ iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j NOTRACK
$ iptables -t raw -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -j NOTRACK
$ iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -j NOTRACK
$ iptables -t raw -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j NOTRACK
3. Conclusion
Timeout connectioncan’t be a disk issue, if it’s disk issue, it will reportServer Internal Errorfrom monitoring probe.Iptables 4 Table 5 Chains: 4 table: raw–>mangle–>nat–>filter . 5 Chain: PREROUTING, INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT, POSTROUTING.- When we don’t need to do NAT, we can use
RAW table to increase performance(eg. Web port). But we need extra DDoS protection method. Remember we need bidirectionalNOTRACKsetup onRAWtable. - Use
sysctl -w net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=262144to solve it immediately. Size calculation, pls refer to above equation.
Ref:
- http://www.pc-freak.net/blog/resolving-nf_conntrack-table-full-dropping-packet-flood-message-in-dmesg-linux-kernel-log/
- http://people.netfilter.org/pablo/docs/login.pdf
- https://wiki.mikejung.biz/Sysctl_tweaks#net.core.netdev_max_backlog
- http://blog.51cto.com/wushank/1171768
- http://www.361way.com/%E5%86%8D%E7%9C%8Bnf_conntrack-table-full%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98/2404.html